A rad is that amount of radiation that:
a. produces 2.08 × 10^9 ion pairs per cm3 in air under standard conditions.
b. deposits 8.76 × 10^–3 J of energy into 1 kg of air.
c. deposits 10–2 J of energy into 1 kg of absorbing material.
d. is also known as a rem.
c
You might also like to view...
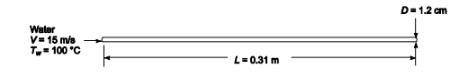
Calculate the maximum safe heat flux in the nucleate-boiling regime for water flowing at a velocity of 15 m/s through a 1.2-cm-ID tube 0.31-m-long if the water enters at 100 kPa pressure and 100°C saturated liquid.
GIVEN
? Nucleate boiling of water flowing through a tube
? Water velocity (V) = 15 m/s
? Tube inside diameter (D) = 1.2 cm = 0.012 m
? Tube length (L) = 0.31 m
? Water pressure (p) = 1 atm
? Water temperature (Tw) = 100°C
FIND
? The maximum safe heat flux in the nucleate boiling regime (q"max)
ASSUMPTIONS
? Steady state
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 13, for water at 100°C, 1 atm

From Appendix 2, Table 35, for steam at 100°C: pv = 0.5977 kg/m3
From Table 9.2: Surface tension at 100°C (s) = 0.0589 N/m
From Table 9.1: For water on copper, Csf = 0.0130
When we see that a spectral line of a galaxy is broadened, that is, spanning a range of wavelengths, we conclude that
A) we do not have very good resolution of a star's orbital velocity. B) there are many stars traveling at extremely high orbital velocities. C) there are different Doppler shifts among the individual stars in the galaxy. D) we are actually measuring the orbital velocity of a cloud of atomic gas. E) we are actually measuring the orbital velocity of dark matter.
For this situation, I push on a heavy chair.Suppose I push lightly on the chair, and the chair doesn't move at all. Then the strength of the force the chair exerts on me is
a. less than the force I exert on the chair. b. equal to the force I exert on the chair. c. greater than the force I exert on the chair. d. zero.
The interior layer just below the crust of Earth is called the ________.
A. inner core B. mantle C. troposphere D. outer core