Majority-rule voting, special-interest group effects, rational voter ignorance, bureaucratic inefficiency, and the shortsightedness effect
A. reflect irrational behavior by the general population.
B. are public choice theories that explain why the public sector might fail to achieve efficient policies.
C. explain why democratic societies need elected officials.
D. are the causes of efficient public policy decisions.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The significant difference between adverse selection problems and moral hazard problems is
a. that adverse selection refers to bad luck, moral hazard refers to bad behaviors. b. that adverse selection applies to markets for goods, moral hazard applies to markets for services. c. only identifiable after an action has been taken. d. that in adverse selection one group of people starts out at a higher risk, while in moral hazard problems, people incur additional risks.
Use the following figure to answer the question below.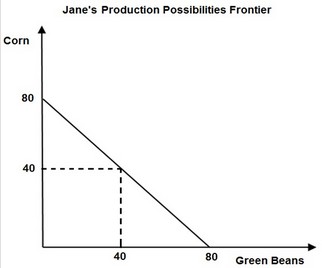 Jane's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of corn is ________ pound(s) of green beans.
Jane's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of corn is ________ pound(s) of green beans.
A. 4 B. 2 C. 1/2 D. 1
When Ford decides to increase production of hybrid cars, it directly answers the ________ question
A) what B) how C) for whom D) where E) why
Fractional reserve banking takes its name from the fact that banks
a. hold only a fraction of their reserves at the bank itself. b. keep only a fraction of their total deposits on reserve. c. lend only a fraction of their total reserves to customers. d. reserve only a fraction of their activity for lending.