As a 1.0-kg object moves from point A to point B, it is acted upon by a single conservative force which does ?40 J of work during this motion. At point A the speed of the particle is 6.0 m/s and the potential energy associated with the force is +50 J. What is the potential energy at point B?
a. +72 J
b. +10 J
c. +90 J
d. +28 J
e. +68 J
c
You might also like to view...
Rotational Kinetic Energy: A solid uniform 3.33-kg disk has thin string of negligible mass wrapped around its rim, with one end of the string tied to the ceiling, as shown in the figure. The disk is released from rest, and as it falls, it turns as the string unwraps. At the instant its center has fallen 2.25 m, (a) how fast is the center moving, and (b) how much rotational kinetic energy does the disk have?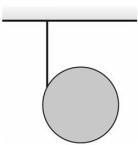
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the above illustrations shows an acidic aqueous solution?
A) A B) B C) C D) All of the above are neutral solutions. E) none of the above
Calculate the entropy of mixing for 2 moles of an alloy that has a composition of 30 atomic %copper and 70 atomic %nickel.
What will be an ideal response?
Why do models suggest that Uranus and Neptune formed elsewhere?
A) We do not have very good models. B) The density of materials was too low in their current orbits for the ice giants to have formed there. C) Jupiter and Saturn took up most of the material in the area; Uranus and Neptune must have formed elsewhere. D) It is too cold at their current locations for the ice giants to have formed there.