When the price is $2
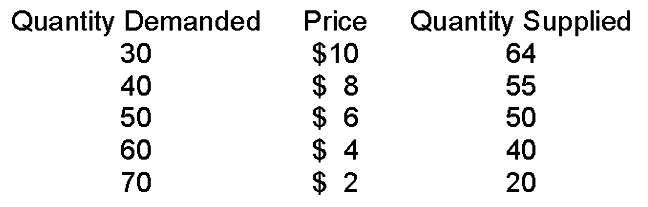
A. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium.
B. quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded and, therefore, price must fall to get to equilibrium.
C. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium.
D. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must fall to get to equilibrium.
C. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium.
You might also like to view...
The profit-maximizing output for the perfectly competitive firm occurs at the point at which
A) TR - MR is at a maximum. B) TR - TC is at a minimum. C) MR = MC. D) TR - ATC is at a maximum.
One example of Ricardian rent is:
a. rent paid to landlords under price controls. b. the difference between the price of a highly demanded unique piece of artwork and the opportunity cost of maintaining it. c. the amount paid to a seller above the equilibrium price of tourist class tickets in order to receive higher quality seats in first class. d. the price rise of wool from a disease among sheep.
In 2005, about 5 percent of all members of the U.S. labor force were holding more than one job. This is called moonlighting. To reduce unemployment, should the government ban moonlighting?
What will be an ideal response?
Since the demand for labor depends on the demand for the product labor produces, the demand for labor is called:
a. primary demand. b. secondary demand. c. dependent demand. d. derived demand.