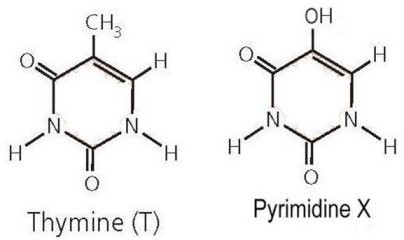
 Consider the structure of thymine, shown on the left in Figure 2.3 above, and compare to the structure of pyrimidine X on the right. What would be the impact if X is incorporated into the structure of a DNA strand in place of thymine?
Consider the structure of thymine, shown on the left in Figure 2.3 above, and compare to the structure of pyrimidine X on the right. What would be the impact if X is incorporated into the structure of a DNA strand in place of thymine?
What will be an ideal response?
Where thymine has a nonpolar group, pyrimidine X has a polar functional group. If incorporated into a DNA strand pyrimidine X would not form the proper hydrogen bonds with either A or G, resulting in mismatches between DNA strands or, more seriously, disruption of the DNA strand. This type of alteration can lead to mutations in the DNA.
You might also like to view...
The difference between a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and a point mutation is that:
A. a point mutation becomes permanently incorporated into the genome, whereas a SNP does not. B. a SNP becomes permanently incorporated into the genome whereas a point mutation does not. C. a point mutation can be corrected by various repair mechanisms, whereas a SNP cannot. D. a SNP can be corrected by various repair mechanisms, whereas a point mutation cannot. E. a point mutation is when a base pair is changed to a different base pair, whereas a SNP is when the base pair differs among individuals in a population.
Isotopes that are unstable and decay when their nucleus breaks up into elements with lower atomic numbers, emitting significant amounts of energy in the process, are called:
A. energetic B. ionic C. radioactive D. isometric
The sex chromosome composition of a person with Turner syndrome is most accurately written as
a. XXX. b. XO. c. XXY. d. XYY. e. X.
Species of fossil organisms are morphospecies, which means they are defined on the basis of ________
A) DNA sequence similarities B) mate recognition behaviors C) anatomical features D) ability to interbreed E) the locations where they are found