This structure of the extensor mechanism lies volar to the axis of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and dorsal to the axis of the PIP
a. Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
b. Lumbricles
c. Oblique retinacular ligament (ORL)
d. Transverse retinacular ligament
ANS: C
The FDP stays volar to both joints while the lumbricles traverse to the dorsal surface at the MP joint. The ORLs begin volar and just before the distal interphalangeal (DIP) move dorsally to blend with the extensor hood.
You might also like to view...
You are treating a 19-year-old who is exhibiting the following symptoms: anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, hyperthermia, tachycardia, and diaphoresis. Upon further investigation, his mother states that her son has not had a drink in three days. What condition are you most likely dealing with?
A) Schizophrenia B) Bipolar disorder C) Delirium tremens D) Panic attack
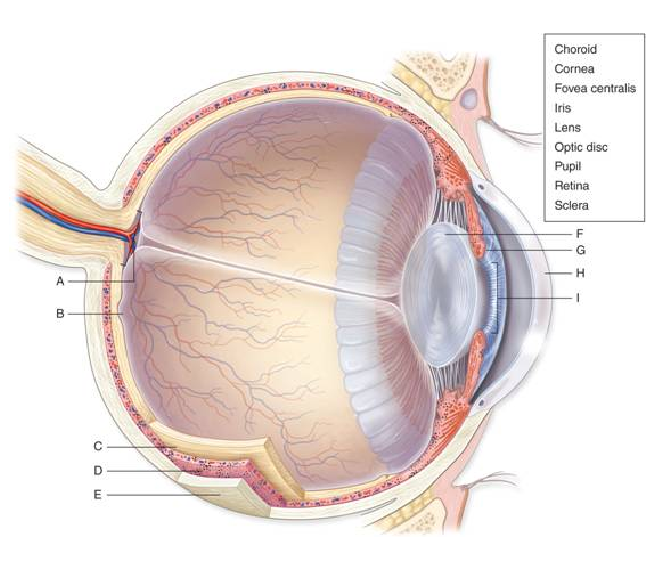
The ________, shown at letter G in the figure, controls the size of the pupil.
If a patient shows signs of fainting, first complete the draw, and then have the patient lie down.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Convert the following temperatures to either Celsius or Fahrenheit. 13°C
What will be an ideal response?