Series/Parallel Circuits: In the circuit shown in the figure, the resistor R has a variable resistance. As R is decreased, what happens to the currents?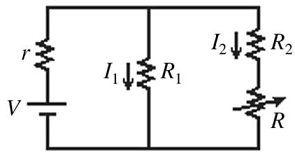
A. I1 remains unchanged and I2 increases.
B. I1 decreases and I2 decreases.
C. I1 decreases and I2 increases.
D. I1 increases and I2 decreases.
E. I1 increases and I2 increases.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following does not provide evidence that Mars once had large amounts of liquid water on its surface?
A) the presence of what looks like dried-up riverbeds B) the presence of impact craters that appear to have formed in mud C) the vast canal system described by Percival Lowell D) the presence of minerals, dry clay, and sedimentary rock that form in water E) some very old craters that appear to have been eroded by rain
Consider a container of 2.0 grams of hydrogen (one gram mole). Suppose you removed all the electrons and moved them to the other side of the Earth (Earth diameter 12740. Km)
(a) How much charge is left behind? (b) What is the attractive force between the protons here and the electrons at the other side of the Earth?
An electron (m = 9.1 × 10^-31 kg) has a speed of 0.90 c. What is the difference between its relativistic momentum and its non-relativistic momentum (in kg m/s)?
a. 4.3 × 10^-22 b. 3.2 × 10^-22 c. 5.4 × 10^-22 d. 6.5 × 10^-22 e. 2.5 × 10^-22
A metal blade (length = 80 cm) spins at a constant rate of 10 radians/s about a pivot at one end. A uniform magnetic field of 2.0 mT is directed at an angle of 30° with the plane of the rotation. What is the magnitude of the potential difference between the two ends of the blade?
a. 5.5 mV b. 6.4 mV c. 3.2 mV d. 11 mV e. 13 mV