The product life cycle theory of comparative advantage predicts that a new product will first be produced and exported by:
a. the nation that was first to demand the new product.
b. the first firm to successfully copy the technology.
c. the nation in which it was invented.
d. the countries with the most stable economy and fewest restrictions on foreign trade.
e. the company with the most extensive network of international distributors for the product.
c
You might also like to view...
The marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS) along an isoquant:
A) is equal to the price ratio at all points along an isoquant. B) is equal to the ratio of the marginal utilities of the two goods. C) is equal to the ratio of the marginal products of the two inputs. D) remains constant as we alter the combinations of the two inputs.
The figure below shows the marginal benefit curves for the two firms in an industry, Firm 1 and Firm 2. Which of the statements below is correct?
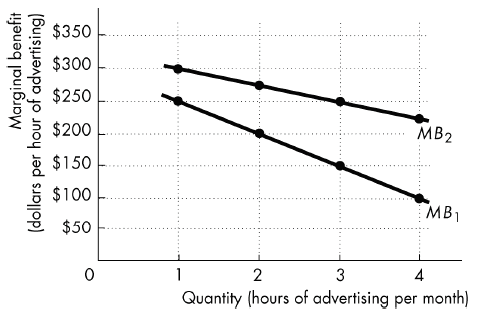
A) At $250, the industry-wide marginal benefit from advertising is 4 hours.
B) The industry-wide marginal benefit from 1 hour of advertising is $300.
C) The industry-wide marginal benefit from 1 hour of advertising is $550.
D) None of the above statements is correct.
When firms are faced with making strategic choices to maximize profit, economists typically use
a. the theory of monopoly to model their behavior. b. the theory of aggressive competition to model their behavior. c. game theory to model their behavior. d. cartel theory to model their behavior.
Which of the following people believes in the ability-to-pay principle?
a. Janice says everyone should pay the same percentage of taxes regardless of what they do or earn. b. Jeannie says that people who earn more money can afford to and should pay more taxes. c. Jay says that people should pay taxes based on how many government services they actually use. d. Jed says that poorer people should pay more taxes because wealthy people use their money to create jobs for the poor.