Which of the following is a main political objection against using the market to reduce pollution?
A. Pollution charges and cap-and-trade schemes raise prices and lower consumer welfare.
B. Cap-and-trade redistributes income from less-efficient polluters to more-efficient polluters.
C. Firms already pay a high corporate tax.
D. Consumers do not have the same built in tax loopholes as firms.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Suppose purchasing power parity holds. If the price level in the United States is 100 dollars per good and the price level in Japan is 250 yen per good, then the nominal exchange rate is ________ yen per dollar
A) 0.25 B) 0.4 C) 2.5 D) 4.0
Many developing countries face a balance of payments constraint because:
A. they fail to implement exchange rate policy correctly. B. they hold too few international reserves. C. they hold too many international reserves. D. the IMF forces them to adopt policies that are counterproductive.
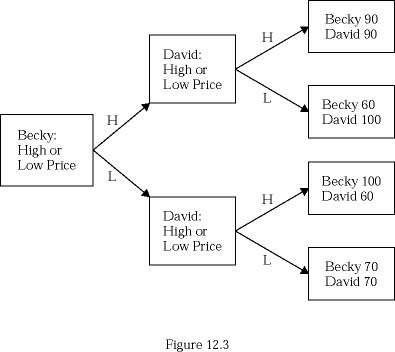 The incentive to charge a low price even though it leads to lower profits in Figure 12.3 is an example of:
The incentive to charge a low price even though it leads to lower profits in Figure 12.3 is an example of:
A. the duopolists' dilemma. B. tying products. C. scarcity and choice. D. the economic problem.
A firm's capital is measured as a ________ while investment in new capital is measured as a ________.
A. flow; stock B. stock; change C. stock; flow D. physical amount; dollar value