Suppose that a vaccine is developed for a highly contagious strain of flu. The likelihood that anyone will get this flu decreases as more people receive the vaccine. One of the demand curves below represents the private demand for the vaccine and the other represents the social demand for the vaccine.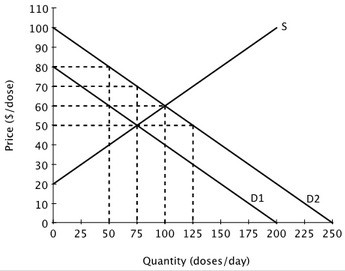 The government could increase total economic surplus by:
The government could increase total economic surplus by:
A. subsidizing production of the vaccine.
B. providing 250 doses of the vaccine for free.
C. taxing production of the vaccine.
D. encouraging people to pay each other to get the vaccine.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
In the Brander-Spencer model the subsidy raises profits by more than the subsidy because of
A) the "multiplier" effect of government expenditures. B) the military-industrial complex. C) the forward and backward linkage effects of certain industries. D) the deterrent effect of the subsidy on foreign competition. E) the economies of scale once the company enters the market.
What happens to the output gap, the real interest rate, and net capital flows with the occurrence of each of the following events? Assume that exchange rates are flexible
a. The Federal Reserve increases the money supply. b. U.S. net exports decrease due to a decrease in incomes in Canada. c. Consumers decide to save more and spend less. d. Expected profits from newly-built factories in the United States decrease.
Which of the following is a reason why the growth rates of high-income countries can be lower than that of low-income countries?
a. In high-income countries, the invention of new technology is difficult, expensive, and time consuming. b. In high-income countries, the invention of new technology is subject to diminishing marginal returns. c. In high-income countries, the marginal cost of production increases as output increases. d. In high-income countries, the average cost of production increases as output increases.
The pessimistic view of the shape of the Environmental Kuznets Curve is
a. linear from the origin b. an inverted-U shape that flattens out after some critical income level c. a perfectly symmetric inverted-U shape d. a flattened U-shape