Figure 15-3
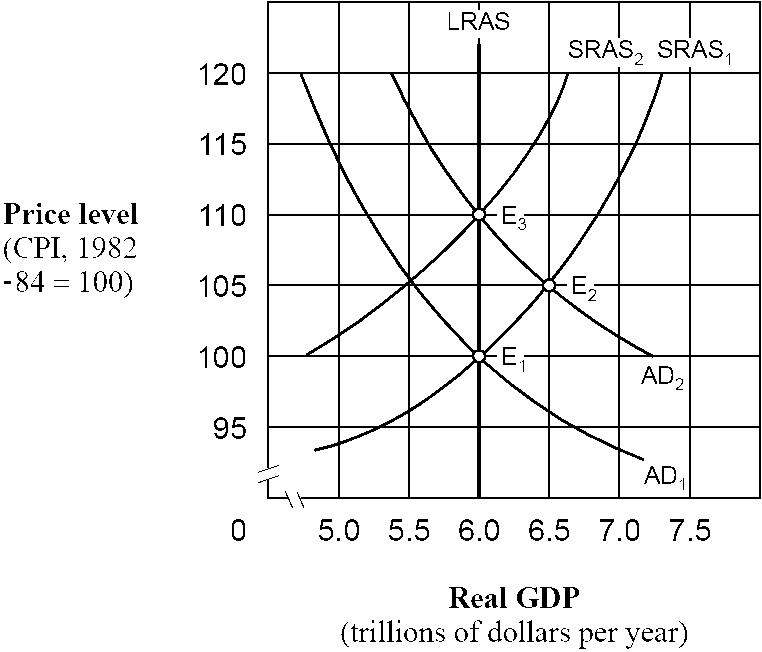
As shown in , if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move
a.
directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
b.
directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
c.
from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
d.
from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.
d
You might also like to view...
Suppose you decide to attend summer school and that this is considered a rational choice. When making this choice,
A) you considered the marginal cost and marginal benefit of your choice. B) you must ignore the problem of scarcity. C) you must have considered the social interest. D) you have made a positive statement. E) you have used the ceteris paribus assumption.
Which of the following is true of capital deepening?
a. It refers to an increase in the level of capital per worker in a society. b. It refers to an increase in the stock of capital in a society c. It occurs when there is a decrease in the cost of capital in a society. d. It occurs when society displaces human capital with physical capital.
When does the degree of international capital mobility affect the qualitative change in the exchange rate (assume flexible exchange rates)?
a. The degree of international capital mobility is important when analyzing changes in monetary policy. b. The degree of international capital mobility is important when analyzing changes in fiscal policy. c. The degree of international capital mobility never affects the qualitative change in the exchange rate. d. The degree of international capital mobility affects the qualitative change in the exchange rate when analyzing changes in the monetary policy as well as changes in the fiscal policy.
Guns and butter represent the classic societal tradeoff between spending on which two items?
a. national defence and consumer goods b. imports and exports c. law enforcement and agriculture d. durable and nondurable goods