The speed–torque characteristic of an induction motor has been empirically determined as follows:
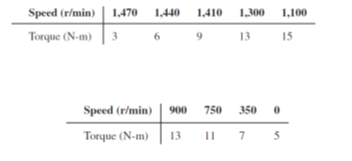
The motor will drive a load requiring a starting torque of 4 N-m and increase linearly with speed to 8 N-m at 1,500 r/min.
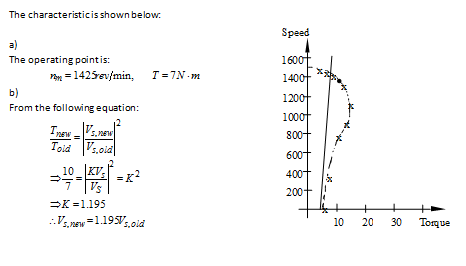
a. Find the steady-state operating point of the motor.
b. Equation 19.68 predicts that the motor speed can be regulated in the face of changes in load torque by adjusting the stator voltage. Find the change in voltage required to maintain the speed at the operating point of part a if the load torque increases to 10 N-m.
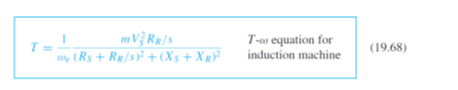
Analysis:
You might also like to view...
The measurements in the table shown in Figure P12–6 were surveyed on a grid for a borrow pit. The first column in the table represents the grid location. “Existing Elevation” is the elevation before excavation, and “Finish Elevation” is the elevation after excavation. The grid spacing is 20?. Grid lines A–F run north and south. Draw the borrow pit grid to scale on an ANSI B size
sheet. Label the grid values and label the cut depths at each grid intersection. Calculate the total amount of excavated material in cubic yards and place the value on the drawing. What will be an ideal response?
When EK = 5.38 m, determine the length of GK. Round the answer to 3 significant digits.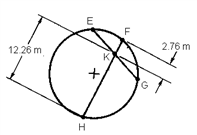
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Residual parent materials have generally been subjected to weathering for a longer period of time than have lacustrine or alluvial parent materials
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The vehicle body can be made from steel, aluminum, fiberglass, plastic, or composite.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)