In a perfectly competitive market, if all firms face identical, constant marginal cost curves, then consumer surplus is
A. definitely zero.
B. the area under the market demand curve and above the market clearing price.
C. the total area under the market demand curve.
D. the area above the market demand curve and above the market clearing price.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
All of the following are examples of product-specific services except which one?
A) displaying a product B) offering the lowest price for the product C) demonstrating a product D) providing information about the product
Hal is the CEO of a firm with a monopoly on a gadget used by kayakers. Hal sells about 200,000 of his products annually, but he would like to make twice that amount available at the same price, hoping to double his income. If we look at the demand curve for Hal’s firm, what will happen as he produces twice as many products?
a. The curve will become vertical. b. The curve will slope upward. c. The curve will slope downward. d. The curve will remain horizontal.
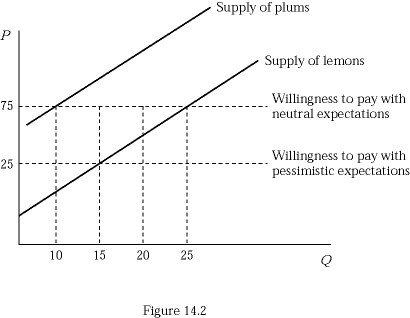 Figure 14.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer cameras are sold in equilibrium?
Figure 14.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer cameras are sold in equilibrium?
A. 10 B. 15 C. 20 D. 25
According to Thomas Robert Malthus, the wage rate would be depressed to the subsistence level because of
A. the power of monopolies. B. the desire of capitalists to exploit the working class. C. the natural tendency of population to grow more rapidly than the production of food. D. the long-run downward trend in investment.