Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.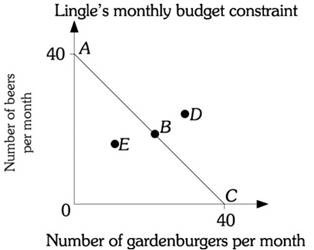 Figure 6.2Refer to Figure 6.2. Mr. Lingle's budget constraint is AC. Point C is
Figure 6.2Refer to Figure 6.2. Mr. Lingle's budget constraint is AC. Point C is
A. an available option and Mr. Lingle exactly spends all of his income.
B. not in Mr. Lingle's opportunity set but is on his budget constraint.
C. an available option and Mr. Lingle does not spend all of his income.
D. not available because it represents a combination of gardenburgers and beer that Mr. Lingle cannot purchase with his current income.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If the quantity demanded for a product exceeds the quantity supplied, the market price will rise until
A) the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The product will then no longer be scarce. B) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The market price will then equal the equilibrium price. C) only wealthy consumers will be able to afford the product. D) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price will then be greater than the market price.
Why do most economists favor emissions taxes and transferable pollution rights over compliance standards as pollution deterrents?
Suppose that the Federal Reserve is concerned about rising inflation, so they increase short- term interest rates. How will this affect long-term rates and the yield curve? What does the slope of the yield curve reveal about the effectiveness of the Fed's policy? Explain in the context of the Liquidity Premium Theory.
What will be an ideal response?
Agricultural subsidies are known to cause overproduction and create other problems. Are there benefits from such subsidies? Explain
What will be an ideal response?