Compare the standard modern theory of international trade that assumes increasing marginal costs with the constant-cost assumption about production costs used in the Ricardian approach.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: In the Ricardian approach, the marginal costs of producing one good as measured in terms of what must be given up to produce other goods is constant. This is illustrated using the straight-line production-possibilities curve (PPC) with a constant slope that shows the combinations of amounts of different products that a country can produce, given the country's available resources. With the more realistic assumption of increasing marginal costs, as the production one good expands at the expense of others, increasing production of the amounts of the other goods must be given up. With increasing marginal costs, the PPC is "bowed out." This reflects that, to produce more of one good, the country must give up increasing amounts of all other goods. This is because the production of different goods uses factor inputs in different proportions.
You might also like to view...
If the inflation rate is negative, the price level in an economy is
A) falling. B) rising slowly. C) constant. D) rising rapidly.
Amusement Park / Cola Tie-in The Six Flags Over Texas amusement part in the middle of the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex has a tie-in marketing campaign with Coca-Cola during the summer. In local grocery stores, some Coke cans offer $5 off admission to the park. Why does Six Flags limit these cans so that none are sold further than 20 miles from the park?
Network effects occur when the value of a platform to its users changes as the number of users rises.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Figure 7-5
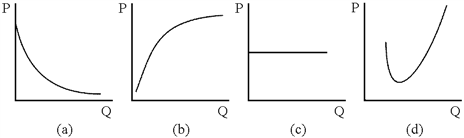
Which of the curves in Figure 7-5 could be a firm's average fixed cost curve?
a.
(a)
b.
(b)
c.
(c)
d.
(d)