Consider the accompanying diagram, which shows an investor who can choose to hold the risky assets on the efficient set and/or the risk-free asset labeled R.
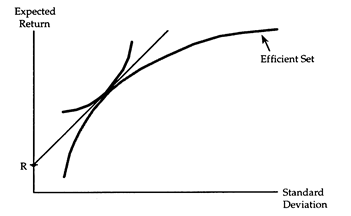
(i) Describe the portfolio held by this investor.
(ii) Suppose the expected return of the risk-free asset increases. Complete the diagram to show how the investor responds to this change. Describe how the market portfolio changes, and describe the new portfolio held by the investor.
(iii) Assume that as the investor's income rises, he prefers that his portfolio have a higher expected return and a lower standard deviation. When the expected return of the risk-free asset rises, does the expected return of the investor's portfolio rise or fall? Does the standard deviation of the investor's portfolio rise or fall? Explain, using substitution and income effects.
(i) Describe the portfolio held by this investor.
(ii) Suppose the expected return of the risk-free asset increases. Complete the diagram to show how the investor responds to this change. Describe how the market portfolio changes, and describe the new portfolio held by the investor.
(iii) Assume that as the investor's income rises, he prefers that his portfolio have a higher expected return and a lower standard deviation. When the expected return of the risk-free asset rises, does the expected return of the investor's portfolio rise or fall? Does the standard deviation of the investor's portfolio rise or fall? Explain, using substitution and income effects.
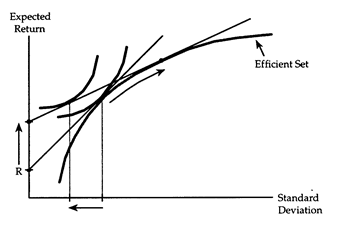
(iii) When the expected return of the risk-free asset rises, the market line becomes flatter. The subsequent substitution effect causes the investor to want a lower expected return and a lower standard deviation in his portfolio. The investor's real income rises, so the income effect causes the investor to want a higher expected return and a lower standard deviation in his portfolio. Thus, the standard deviation of the investor's portfolio must fall, but its expected return could either rise or fall.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following pairs of goods is likely to be considered complements?
A) Nokia and Samsung cell phones B) Laptops and electric heaters C) Motorcycles and typewriters D) Pens and writing pads
Monopolist fears that central banks would unfairly compete with all other profit-maximizing banks contributed to the demise of the First and Second Banks of the U.S
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
When a country has a large amount of dead capital
A) there is too much political freedom. B) there is a large amount of economic growth. C) large amounts of capital will be inefficiently employed. D) a country's exports increase.
Which of the following is an example of a near-public good?
a. a highway b. clean air c. a gallon of milk d. pollution e. a ticket to a professional baseball game