Suppose the Sun were to suddenly shrink in size but its mass remained the same. According to the law of conservation of angular momentum, what would happen?
A) The Sun's angular size in our sky would increase.
B) The Sun's rate of rotation would slow.
C) The Sun's rate of rotation would remain the same.
D) The Sun rate of rotation would increase.
D) The Sun rate of rotation would increase.
You might also like to view...
Imagine an advanced civilization living on a planet orbiting at a distance of 10 AU (1.5 billion kilometers) from a close binary star system that consists of a 15 MSun red giant star and a 10 MSun black hole
The black hole is surrounded by an accretion disk. Sometime within the next million years or so, the civilization's planet is likely to be doomed because A) the red giant will probably supernova within the next million years. B) jets of material shot out of the accretion disk will shoot down their planet. C) the red giant star, which provides most of energy the civilization needs to exist, will soon be destroyed in the accretion disk. D) tidal forces from the black hole will rip the planet apart.
You are told that 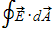
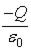

A.
B.
C.
D.
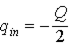 .
.E.
Studies from ________ led to the discovery of "dark energy."
A) Type II supernovae in the Large Magellanic Cloud B) Cepheid variables in the Virgo Cluster C) the COBE microwave ripples D) the gravitational lensing by MACHOs E) Type I supernovae at very large redshifts
A small metal sphere is suspended from the conducting cover of a conducting metal ice bucket by a non-conducting thread. The sphere is given a negative charge before the cover is placed on the bucket. The bucket is tilted by means of a non-conducting material so that the charged sphere touches the inside of the bucket. Which statement is correct?
a. The negative charge remains on the metal sphere. b. The negative charge spreads over the outside surface of the bucket and cover. c. The negative charge spreads over the inside surface of the bucket and cover. d. The negative charge spreads equally over the inside and outside surfaces of the bucket and cover. e. The negative charge spreads equally over the sphere and the inside and outside surfaces of the bucket and cover.