Discuss the four stages of mitosis
What will be an ideal response?
1. Prophase—chromatin threads coil and shorten so that visible bar-like bodies, called chromosomes, appear. Each chromosome is made up of two strands, called chromatids, which are held together by a centromere. Additionally, the centrioles separate and move toward opposite sides of the cell, directing the assembly of the mitotic spindle (composed of microtubules) between them as they move.
2. Metaphase—the chromosomes cluster and align in the center of the spindle, midway between the centrioles, forming a straight line of chromosomes.
3. Anaphase—the centromeres split and the chromosomes move slowly apart toward opposite ends of the cell. A cleavage furrow appears over the midline of the spindle and eventually pinches the cytoplasmic mass into two parts in a process called cytokinesis.
4. Telophase—the chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell and their movement ends, and they then uncoil and become chromatin again. A nuclear membrane then forms around each chromatin mass, the spindle breaks down and disappears, and nucleoli re-appear in each of the daughter nuclei. Finally, cytokinesis produces two separate daughter cells.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is part of the pelvic girdle?
A. the ilium B. the ischium C. the pubis D. all of the above
The lowest level of cells of the strata, marked E, consists of
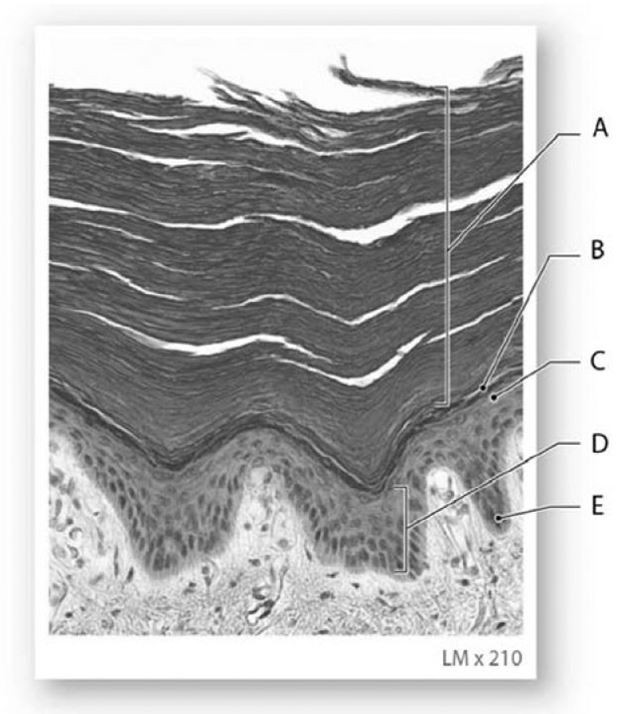
A) keratin protein.
B) collagen fibers.
C) dead cells.
D) carotene-producing cells.
E) mitotically active epithelial cells.
A synchondrosis is a cartilaginous joint
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Glyc/o- is the combining form for sugar.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)