The charge cycle shown in Figure P2.4 is an example of a three-rate charge. The current is held constant at 30 mA for 6 h. Then it is switched to 20 mA for the next 3 h.
Find:
a. The total charge transferred to the battery.
b. The energy transferred to the battery.
Hint: Recall that energy w is the integral of power, or P = dw/dt.
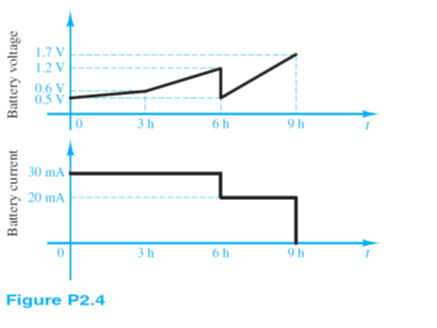
a) Current is equal to 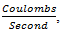 therefore given the current and a duration of that current, the transferred charge can be calculated by the following equation:
therefore given the current and a duration of that current, the transferred charge can be calculated by the following equation:
A •t = C
The two durations should be calculated independently and then added together.
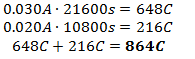
b) P=V•I, therefore, an equation for power can be found by multiplying the two graphs together.
First separate the voltage graph into three equations:

You might also like to view...
? Identify and state the historical significance of Robert S. McNamara.
What will be an ideal response?
Some seeds have a hard seed coat that must be soaked or scratched before the seeds are able to germinate
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Torque multiplication is possible when a torque converter is in this mode:
a. rotary flow b. vortex flow c. lock up d. dual phase
Which of the following restrictions are best used for measuring fluids that contain solid particles?
A. orifice B. flow nozzle C. venturi