An unintended consequence of price ceilings is:
A. the loss of surplus always outweighs the benefits of the policy.
B. non-price rationing must occur, and can lead to bribes.
C. the transfer of surplus from producer to consumer rarely is recognized.
D. the producers increase the quality of the goods sold.
B. non-price rationing must occur, and can lead to bribes.
You might also like to view...
Suppose there are two goods: guns and roses. Also suppose Australia is initially closed to trade. When international trade is opened, Australia chooses to sell guns and buy roses in the world markets.
(i) Which is higher, Australia's autarkic relative price of guns or the world relative price of roses? (ii) If the world relative price of guns falls, will Australia be better off or worse off? What if the world relative price of guns rises? Explain.
Which of the following is likely to be used as a signal in the job market?
A) The job description B) The degree obtained by the applicant C) The letter of appointment D) An announcement of vacancy
Because the cost of healthcare as a percent of GDP rises and as a result productivity gains tend to fall, it is said the healthcare industry suffers from ________________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.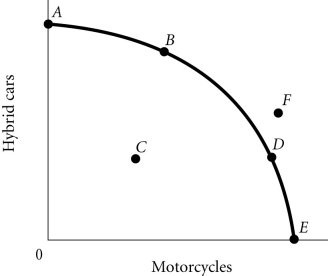 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point F
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point F
A. is efficient and attainable. B. cannot be produced with the current state of technology. C. represents underallocation of resources. D. represents what the people want.