In a perfectly elastic collision, a 400-g ball moving toward the east at 3.7 m/s suddenly collides head-on with a 200 g ball sitting at rest. (a) Determine the velocity of the first ball just after the collision
(b) Determine the velocity of the second ball just after the collision. (c) Is kinetic energy conserved in this collision? How do you know?
(a) 1.2 m/s toward the east (b) 4.9 m/s toward the east (c) Yes, it is an elastic collision.
You might also like to view...
__________is the gradual increase in the surface temperature of Earth caused by human modifications to Earth's atmosphere
A) The greenhouse effect. B) Global warming C) Differentiation D) The Tyndall effect
Substitute the correct prefix to the fun-word "1012-tory"
A) milli B) kilo C) giga D) pico E) tera
On an H-R diagram, stellar radii
A) are greatest in the lower left and least in the upper right. B) decrease from left to right. C) are impossible to determine. D) increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right.
A 3.0-kg ball with an initial velocity of 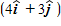
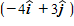
A.
 N
N s
sB.
 N
N s
sC.
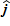 N
N s
sD.
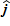 N
N s
sE.
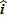 N
N s
s