What is the chief difficulty in attempting to detect planets around other stars?
A) Planets do not emit visible light. They are typically at least a billion times fainter than their host stars.
B) Even the largest planets are typically at least a factor of 10 times smaller than their host stars.
C) Planets do not glow in the infrared, so infrared telescopes cannot be used to study them, either.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a positive subatomic particle?
a. neutron only b. proton only c. electron only d. neutron and proton e. proton and electron
Photon Energy: Two sources emit beams of microwaves. The microwaves from source A have a frequency of 10 GHz, and the ones from source B have a frequency of 20 GHz. This is all we know about the two beams. Which of the following statements about these beams are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A. Beam B carries twice as many photons per second as beam A. B. A photon in beam B has twice the energy of a photon in beam A. C. The intensity of beam B is twice as great as the intensity of beam A. D. A photon in beam B has the same energy as a photon in beam A. E. None of these statements are true.
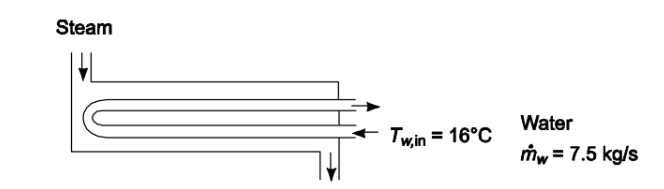
A shell-and-tube heat exchanger with the characteristics given below is to be used to heat 27,000 kg/h of water before it is sent to a reaction system. Saturated steam at 239 kPa absolute pressure is available as the heating medium and will be condensed without subcooling on the outside of the tubes. From previous experience, the steam-side condensing coefficient can be assumed constant and equal to 11,300 W/(m2 K). If the water enters at 16°C, at what temperature will it leave the exchanger? Use reasonable estimates for fouling coefficients. Exchanger specifications
- Tubes – 2.5-cm-OD, 2.3-cm-ID, horizontal copper tubes in six vertical rows
- Tube length = 2.4 m
- Total number of tubes = 52
- Number of tube-side passes = 2
GIVEN
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger - water in copper tubes, saturated steam is shell Water flow rate m w= 27,000 kg/h = 7.5 kg/s Steam pressure = 2.36 atm = 239 kPa Steam-side coefficient h o= 11,300 W/(m2 K) Water entrance temperature: Tw,in = 16°C Tube diameters
? Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
? Di = 2.3 cm = 0.023 m Tube length (L) = 2.4 m Number of tubes (N) = 52 Number of tube passes = 2
FIND
The water exit temperature (Tw,out)
ASSUMPTIONS
Length given is total tube length for both passes
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the temperature of saturated steam at 239 kPa (Ta) = 125°C
for water at 20°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.597 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 1.006 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 7.0 Density (?) = 998.2 kg/m3 Specific heat (cp) = 4182 J/(kg K), the thermal conductivity of copper (kc) = 392 W/(m K) at 127°C
In a two-slit experiment, the third bright fringe away from the central fringe is observed at an angle of 7.0°. If the wavelength of the light is 490 nm, what is the distance between the two slits?
A) 3.6 × 10-5 m B) 4.0 × 10-6 m C) 2.1 × 10-6 m D) 2.1 × 10-5 m E) 1.2 × 10-5 m