The trade-off between risk and expected value is exactly the kind of choice you have to make whenever you think about investing money in:
A. stocks.
B. retirement funds.
C. bonds.
D. One needs to think about the trade-off to invest in all these things.
D. One needs to think about the trade-off to invest in all these things.
You might also like to view...
Suppose that there is only one small clothing store in the remote village of Green Acres, and until recently the townspeople bought their shirts there. As more people in Green Acres become connected to the Internet, the price elasticity of demand for shirts at the Green Acres store will:
A. increase because the Internet offers more substitutes. B. remain the same, but the quantity demanded will decrease as more people shop online. C. decrease because the Internet offers more substitutes. D. remain the same, but the demand will decrease as more people shop online.
What does GDP measure to avoid double-counting?
a. final goods and services b. intermediate goods and services c. net exports d. all sales of goods and services
According to purchasing-power parity, which of the following necessarily equals the ratio of the foreign price level divided by the domestic price level?
a. the real exchange rate, but not the nominal exchange rate b. the nominal exchange rate, but not the real exchange rate c. the real exchange rate and the nominal exchange rate d. neither the real exchange rate nor the nominal exchange rate
Refer to the accompanying figure. Suppose the solid line shows the current demand curve for coffee. In response to an announcement that much of next year's coffee crop has been destroyed by a storm in Brazil, you should expect: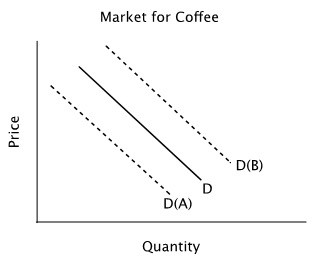
A. an increase in the quantity of coffee demanded, but no shift in the demand curve. B. neither a change in quantity demanded nor a shift in demand because next year's coffee crop will not affect the current demand for coffee. C. the demand curve to shift to D(A) in anticipation of higher future prices. D. the demand curve to shift to D(B) in anticipation of higher future prices.