A ball is thrown upward at a velocity of 19.6 m/s. What is its velocity after 3.00 s?
A. 9.80 m/s up
B. zero
C. 19.6 down
D. 9.80 m/s down
D. 9.80 m/s down
You might also like to view...
A GUT (grand unified theory) refers to theories that
A) unify the electromagnetic and weak forces. B) unify the strong force and the electromagnetic and weak forces. C) unify all four forces. D) unify gravity and the electromagnetic and weak forces. E) unify gravity and the strong and weak forces.
A constant electric field 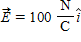
A. 0. B. 0.25. C. 25. D. 50. E. 100.
A rectangular loop (area = 0.15 m2) turns in a uniform magnetic field with B = 0.20 T. At an instant when the angle between the magnetic field and the normal to the plane of the loop is (p/2) rad and increasing at the rate of 0.60 rad/s, what is the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop?
a. 24 mV b. zero c. 18 mV d. 20 mV e. 6.0 mV
Compared to the Earth, the moon is no longer geologically active because
a. it is rotating too slowly. b. its radioactive elements were never abundant. c. it is much smaller in mass. d. its crust is too thin. e. it does not have water on its surface.