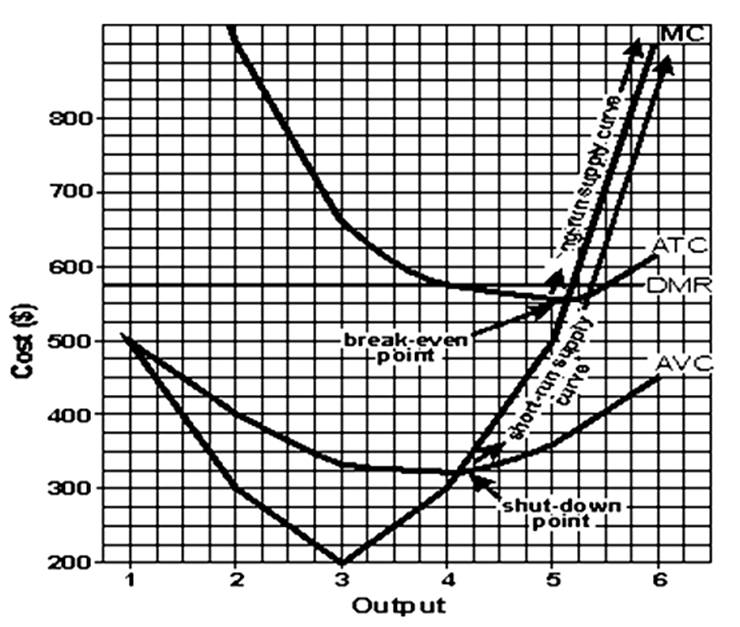
You should do this problem in three steps. First: Fill in Table 1. Assume fixed cost is $1000 and price is $575. Second: Draw a graph of the firm's demand, marginal revenue, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves on a piece of graph paper. Be sure to label the graph correctly. On the graph, indicate the break-even and shutdown points and the firm's short-run and long-run supply curves. Third: Calculate total profit in the space below, then answer questions a through d. (a) The minimum price the firm will accept in the short run is $_______. (b) The minimum price the firm will accept in the long run is $_______. (c) The output at which the firm will maximize profits is _______. (d) The output at which the firm will operate most efficiently is ________.
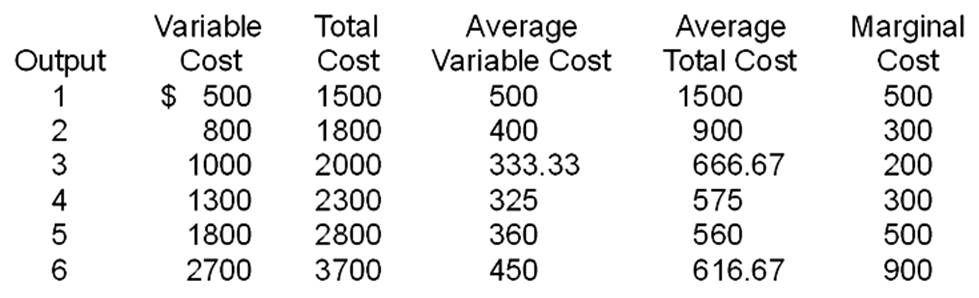
Table 1:

Table 2:


Total profit= (Price - ATC) × output
= ($575 - $560) × 5.2
= $15 × 5.2
= $78 (Must be slightly over $75.)
(a) $324. (b) $558. (c) 5.2. (d) 5.15
Table 2:
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________. 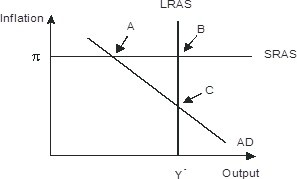
A. Rising; A B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; B: C D. Rising; A; C
Suppose a person's utility for leisure (L) and consumption (Y) can be expressed as U = Y + L0.5. Assuming a wage rate of $10 per hour, show what happens to the person's labor supply curve when the person wins a lottery prize of $100 per day
What will be an ideal response?
The branch of economics that studies the aggregate decisions of all households and all firms is called: a. positive economics
b. normative economics. c. microeconomics. d. macroeconomics.
During 2011, the price level in the U.S. rose at a faster rate than the price level in Japan. Other things the same, according to purchasing-power parity, this difference in inflation rates should have caused
a. the nominal exchange rate of the dollar to appreciate relative to the yen. b. the real exchange rate of the dollar to appreciate relative to the yen. c. the nominal exchange rate of the dollar to depreciate relative to the yen. d. the real exchange rate of the dollar to depreciate relative to the yen.