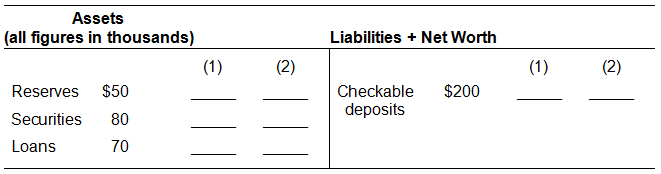
Assume that households and businesses deposit $10,000 in this bank and that this currency is added to the bank’s reserves. In column (1) show the bank’s balance sheet after this occurs. Is there a change in the money supply? In column (2) show what would happen if the bank now loans all of its excess reserves to a depositor. Is there a change in the money supply?
Suppose the Second National Bank has the following simplified balance sheet. The reserve ratio is 25%.
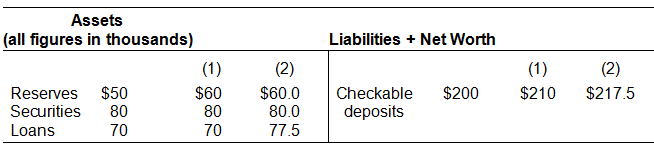
No, currency has been reduced dollar-for-dollar with the $10,000 increase in check able deposits.Yes, the $7500 excess reserves increase check able deposit money by $7500.
You might also like to view...
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is computed as the change in:
a. savings divided by the change in saving. b. savings divided by the change in disposable personal income. c. saving divided by the change in GDP. d. None of these.
If an increase in the price of a product from $1 to $2 per unit leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded from 100 to 80 units, then according to the averaging equation, the value of price elasticity of demand in absolute terms is
a. 0.33 b. 2.33 c. 0.25 d. 3 e. 0.66
Externalities are unintended costs or benefits imposed on third parties. Who creates these externalities?
a. the government b. the market c. the third parties themselves d. buyers create the costs, sellers create the benefits e. the economic activity of others that affects third parties
The use of tax penalties to control pollution represents a
A. price-based market approach to the pollution problem. B. nonmarket approach to the pollution problem. C. major source of current federal revenues. D. pollution-rights solution to the pollution problem.