proportional relationship between a galaxy's distance and that galaxy's receding velocity
A. Gerard de Vaucouleurs |
B. Georges Lemaître |
C. Hubble’s Law |
D. Edwin Hubble |
E. Velocity or Speed |
F. Ho |
C. Hubbles Law
You might also like to view...
Which of the following material states has the highest entropy?
(a) Amorphous solid (b) Vapor (c) Liquid (d) Single crystal
The process of making an electron less tightly bound to an atom's nucleus is known as
a. excitation. b. Doppler broadening. c. collisional broadening. d. a red shift. e. quantum mechanics.
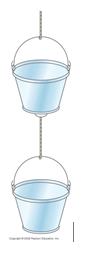
One 3.2-kg paint bucket is hanging by a massless cord from another 3.2-kg paint bucket, also hanging by a massless cord, as shown in the figure
a) If the buckets are at rest, what is the tension in each cord?
b) If the two buckets are pulled upward with an acceleration of 1.25 m/s by the upper cord, calculate the tension in each cord.
Stellar and galactic crowding: The comparison of objects' sizes to the distance between them gives a sense of their relative density, i.e., how "crowded" they are. A typical human is about 1 meter across the shoulders
Compare the relative density of people in the case where they are standing on average 1 meter apart compared to a situation where they are on average 10 meters apart (hint: describe the separation in units of person-size). Now, compare the "crowding" of stars to that of galaxies. A typical star has a diameter of about 1 million km, while the average space between stars is about 5 light-years. A typical spiral galaxy in a cluster (such as the Milky Way) is 100,000 light-years across, and has another spiral galaxy within about 10 million light years.