Double counting in the resource cost-income approach to GDP refers to
a. corporate income being taxed twice
b. the amount of income taxes paid to states that is taxable by the federal government
c. calculating GDP twice using the income and expenditures methods
d. adding the value of exports to GDP and subtracting the value of imports
e. counting the total value of a final output in addition to the value of the inputs used to make it
E
You might also like to view...
Figure 6-2
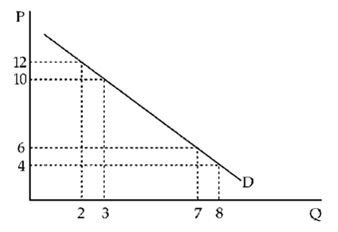
A. smaller; smaller B. smaller; greater C. greater; smaller D. greater; greater
Barriers to entry can be the result of
a. Positive network externalities b. High switching costs c. Economies of scale d. All of the above
Assume that the central bank increases the reserve requirement. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and the nominal value of the domestic currency in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency falls. b. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency remains the same. c. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. d. The GDP Price Index rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. e. The GDP Price Index falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises.
Based on the graphs showing price discrimination in movie ticket prices, if the theatre charges $11 per ticket at the matinee, it will ______.
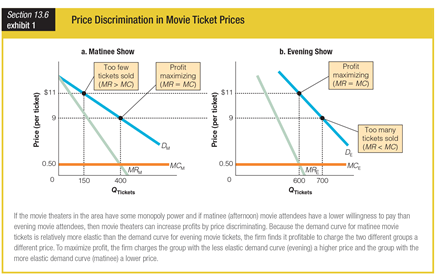
a. maximize profits
b. sell too many tickets
c. sell too few tickets
d. sell no tickets