Refer to Table 5.1. A risk-averse student making a decision solely on the basis of the above information
A) would definitely become a math major.
B) would definitely not become an English major.
C) would definitely become a political science major.
D) might be either a mathematics major or English major, depending upon the utility of the average offer.
E) would definitely be indifferent between the accounting major and the English major if the probability of finding a job in accounting were any value higher than 0.95.
D
You might also like to view...
Penetration pricing is:
A. a way to overcome an incumbent's first-mover advantage. B. ineffective in markets with strong networks. C. a way to raise a rival's fixed cost. D. a way to raise a rival's marginal cost.
What will increase long-run aggregate supply?
What will be an ideal response?
Income mobility:
A. contributes to greater wealth inequality in the United States. B. is less in the United States than in most developing nations. C. is the movement of individuals and households from one income quintile to another over time. D. makes lifetime income inequality among income receivers in the United States greater than income inequality in any single year.
Refer to the diagram where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars. Beta's profits are shown in the northeast corner and Alpha's profits in the southwest corner of each cell. If Beta commits to a high-price policy, Alpha will gain the largest profit by:
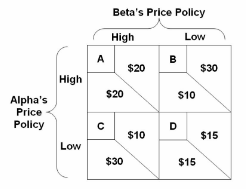
A. also adopting a high-price policy.
B. adopting a low-price policy.
C. adopting a low-price policy, but only if Beta agrees to do the same.
D. engaging in nonprice competition only.