Bill attends a local basketball game. The teams are very unbalanced, the play is bad, and the score quickly reaches 36-2. At halftime, Bill realizes he's having no fun, leaves the game, and goes home. Bill's behavior is NOT determined by
A. sunk costs.
B. utility maximization.
C. economic logic.
D. None of these is true.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If a product has an external benefit, how does its marginal private benefit compare to its marginal social benefit?
A) Marginal private benefit is less than marginal social benefit. B) Marginal private benefit is greater than marginal social benefit. C) At low quantities, marginal private benefit is less than marginal social benefit but at high quantities, marginal private benefit is greater than marginal social benefit. D) At low quantities, marginal private benefit is greater than marginal social benefit but at high quantities, marginal private benefit is less than marginal social benefit. E) Marginal private benefit cannot be compared to marginal social benefit.
If the market mechanism is efficient, the marginal cost accurately measures the opportunity cost of a good or service.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
In 2016 the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that there were 57.1 million people over age 25 whose highest level of education was some college or an associate degree. Of these, 36.4 million were employed and 1.5 million were unemployed. What were the labor-force participation rate and the unemployment rate for this group?
a. 66.4% and 2.6% b. 66.4% and 4.0% c. 63.7% and 2.6% d. 63.7% and 4.0%
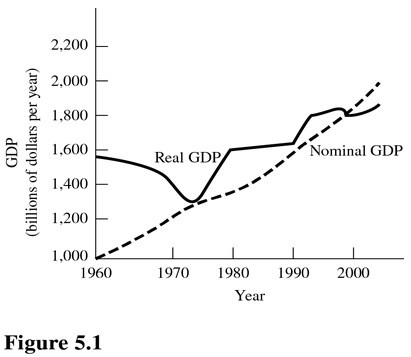 According to the hypothetical economy in Figure 5.1, between 1960 and 1970 real GDP declined but nominal GDP continued to rise. The increase in nominal GDP was due to
According to the hypothetical economy in Figure 5.1, between 1960 and 1970 real GDP declined but nominal GDP continued to rise. The increase in nominal GDP was due to
A. An increase in the standard of living. B. A decrease in the price level. C. An increase in the quantity of output produced. D. An increase in the price level greater than the decrease in output, causing the nominal dollar value of output produced to increase.