A complete spinal cord injury to the upper cervical spine:
A) results in quadriplegia but the patient usually retains his or her ability to breathe spontaneously.
B) is not compatible with life and results in immediate death due to cardiopulmonary failure.
C) will result in permanent loss of all cord-mediated functions below the level of the injury.
D) results in neurologic dysfunction that is considered to be permanent if it lasts longer than 24 hours.
Answer: C) will result in permanent loss of all cord-mediated functions below the level of the injury.
You might also like to view...
The triangle of auscultation is bordered by the rhomboid major, latissimus dorsi, and the ________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
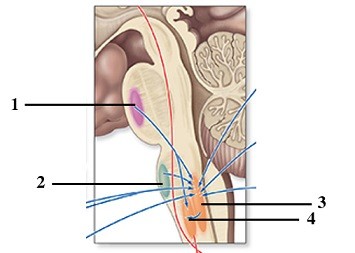 This figure shows respiratory control centers in the brainstem. What does number 3 indicate?
This figure shows respiratory control centers in the brainstem. What does number 3 indicate?
A. Central chemoreceptors B. Dorsal respiratory group C. Pontine respiratory center D. Ventral respiratory group
What is a hematocrit?
A) Quantity of leukocytes in a blood sample B) Percentage of erythrocytes in a blood sample C) Ratio of fibrinogen to fibrin in a blood sample D) Volume of plasma in a blood sample
Which system is home to the organs that produce and secrete hormones?
A. Endocrine B. Nervous C. Reproductive D. Cardiovascular