Opportunity cost is:
A) the costs of all sacrifices not chosen when a choice is made.
B) the highest valued other choice that could have been made.
C) the result of having made a bad choice.
D) the result of not making choices at the margin.
Ans: B) the highest valued other choice that could have been made.
You might also like to view...
Economists may disagree about how to solve an economic problem because they
A. may not be able to use the same models. B. always make the same value judgments. C. are unable to assemble all of the necessary facts about the economy. D. All of these responses are correct.
In the above figure, using the slope across an arc, the slope of the curve between points a and c is
A) 3/5. B) 5/3. C) -3/5. D) -5/3.
The long-run industry supply curve will be upward-sloping if:
A. output prices are fixed no matter what the level of output. B. there are no economies or diseconomies of scale. C. input prices are fixed no matter what the level of output. D. input prices increase with the level of output.
Refer to the graph below showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. If the world price for this product is $2.00, then Econland will:
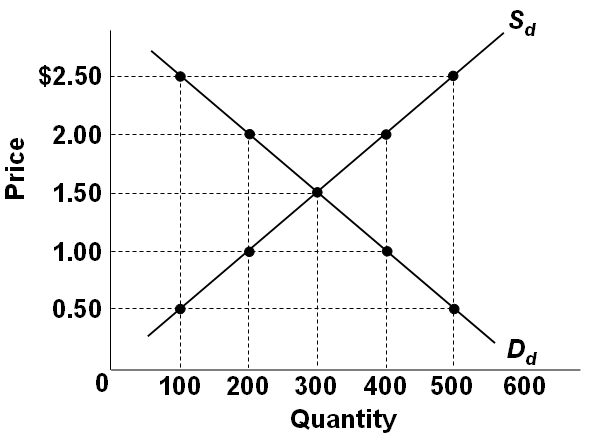
A. Export 200 units
B. Export 400 units
C. Import 200 units
D. Import 400 units