In a closed economy, a decrease in the money supply will
A) shift the aggregate demand schedule to the left.
B) shift the aggregate supply schedule to the right.
C) shift the IS curve to the left.
D) shift the LM curve to the right.
A
You might also like to view...
Suppose that there is a negative aggregate demand shock and the central bank commits to an inflation rate target. If the commitment is credible, then
A) the public's expected inflation will remain unchanged. B) the short-run aggregate supply curve will rise. C) over time inflation will fall. D) all of the above. E) both A and C.
Excessive volatility refers to the fact that
A) stock returns display mean reversion. B) stock prices can be slow to react to new information. C) stock price tend to rise in the month of January. D) stock prices fluctuate more than is justified by dividend fluctuations.
If a perfect competitor faces P = ATC in the long run, the firm will
A) earn economic profits. B) earn economic losses. C) leave the industry. D) remain in the industry.
If the intended aim of the price floor set in the graph shown was a net increase in the well-being of producers, then normative analysis would conclude that:
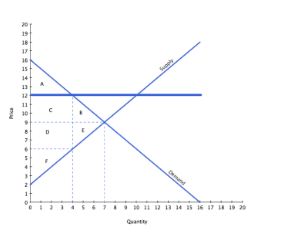
A. the policy was effective, since surplus gained by producers through higher prices is greater than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
B. the policy was ineffective, since surplus gained by producers through higher prices is greater than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
C. the policy was effective, since surplus gained by producers through higher prices is greater than the surplus lost by consumers through higher prices.
D. there is no "right" conclusion to be reached in a normative sense, since people have different opinions concerning what constitutes a better outcome.