In the long run, firms in a monopolistically competitive market operate at:
A. a more-than-efficient scale.
B. an efficient scale.
C. a less-than-efficient scale.
D. Any of these could be true, depending on the individual firm.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the production possibilities frontier in the figure above. Which of the following movements requires the largest opportunity cost, in terms of good Y forgone, per extra unit of good X?
A) from point a to point b B) from point b to point c C) from point c to point d D) from point d to point e
In the above figure, if the wage rate fell below Wb, in the short run the firm would
A) hire more workers. B) fire several workers. C) reduce its level of output. D) keep all its input levels the same as they were before.
A rain barrel is a container that captures and stores rainwater for landscape and garden use during dry periods. Rain barrels provide an external benefit to the community through water conservation. What can the government do to equate the equilibrium quantity of rain barrels and the socially optimal quantity of rain barrels?
a. impose a tax on rain barrels that is equal to the per-unit externality b. offer a subsidy on rain barrels that is equal to the per-unit externality c. encourage homeowners to bargain with rain barrel producers d. nothing
If the economy produces 12 capital goods and 40 consumer goods,
Hypothetical Production Schedule for a Two-Product Economy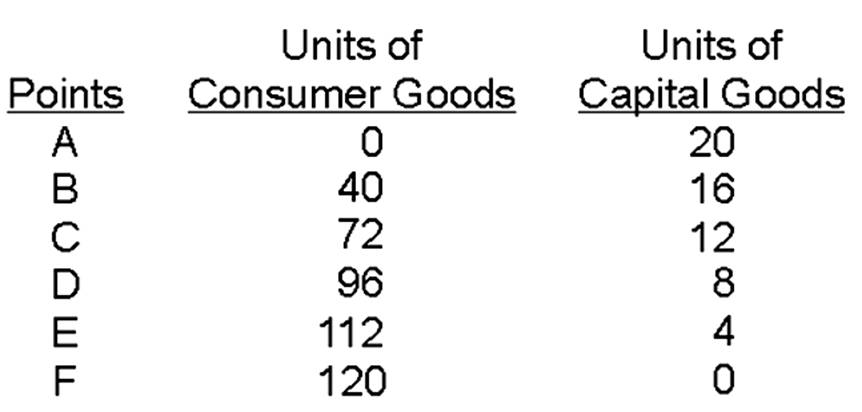
A. it is producing outside its production possibilities curve.
B. this combination of output will most likely result in economic growth.
C. the ability to produce more consumer goods can only be realized by sacrificing capital goods.
D. this economy has some unemployed resources.