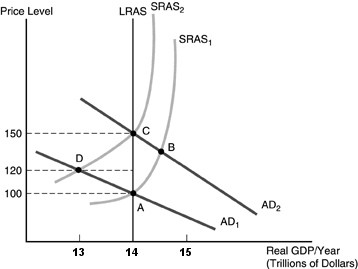
 Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy is in equilibrium at point A. If the Fed tries to stimulate the economy by undertaking an expansionary monetary policy action and this is NOT expected by the people in the economy, we would expect to see
Refer to the above figure. Suppose the economy is in equilibrium at point A. If the Fed tries to stimulate the economy by undertaking an expansionary monetary policy action and this is NOT expected by the people in the economy, we would expect to see
A. aggregate demand increases but people would anticipate this, causing the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift up at the same time, with the new equilibrium of $14 trillion of real GDP and a price level of 100.
B. aggregate supply shifts up as people anticipate the effects of the expansionary monetary system. In the short run, real GDP falls to $13 trillion and the price level rises to 120. In the long run, real GDP returns to $14 trillion, and the price level increases further, to 150.
C. aggregate demand increases, real GDP increases, and the price level increases. In the long run, aggregate supply would increase and the new long-run equilibrium would be point B.
D. aggregate demand increases, real GDP increases, and the price level increases in the short run. In the long run, people realize the real situation, causing the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift up. Real GDP returns to $14 trillion, and the price level increases to 150.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If, at the current exchange rate between the dollar and the South African rand of 6.92 rand per dollar, the dollar is "undervalued," how do you expect demand and supply in the foreign exchange markets to respond?
A) The supply of the dollar will fall, while the demand for the rand will rise. B) The demand for the dollar will rise, while the supply of the rand will fall. C) The demand for the dollar will fall, while the supply of the rand will rise. D) The demand for the dollar will rise, while the supply of the rand will rise.
Economies of scale in nuclear power plants exist because of
A) more efficient plant management. B) a better understanding of the plant's idiosyncrasies, or learning-by-doing. C) nuclear power technology changes. D) both A and B.
If a consumer purchases only two goods (x and y) and the demand for x is elastic, then a rise in the price of x:
a. will cause total spending on good y to rise. b. will cause total spending on good y to fall. c. will cause total spending on good y to remain unchanged. d. will have an indeterminate effect on total spending on good y.
During the Great Depression, the rate of unemployment in the United States reached a high of
a. 10 percent. b. 15 percent. c. 20 percent. d. 25 percent.