If the supply and demand curves below represent the market supply and demand for a purely competitive industry, then the demand curve that an individual firm in the industry faces:
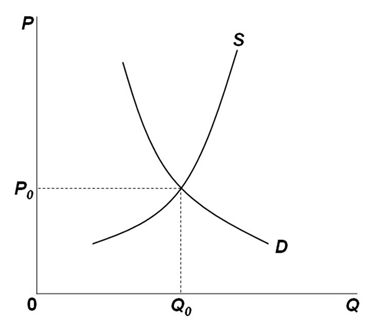
A. Is identical to the market demand
B. Is equal to the marginal-revenue curve which is a flat line at P0
C. Is more elastic than the market demand but has a marginal-revenue curve lying below it
D. Has the same slope as the market demand, but at P0 its quantity demanded is only a fraction of Q0
B. Is equal to the marginal-revenue curve which is a flat line at P0
You might also like to view...
The purchasing power of the dollar
A) varies directly with the purchasing power of other major currencies such as the euro and the Japanese yen. B) varies inversely with the price level. C) varies directly with the price level. D) varies directly with the price of gold.
Assume that the government provides a cash transfer to each family regardless of their market earnings. Given this transfer, which of the following hypotheses about labor supply is correct?
a. Labor supply will increase because the income effect outweighs the substitution effect. b. Labor supply will increase because leisure is an inferior good. c. The income effect will reduce labor supply; there is no substitution effect. d. Labor supply will be constant since wages are unaffected.
All other things held constant, lower marginal (income) tax rates
A) necessarily increase tax revenues. B) necessarily decrease tax revenues. C) decrease the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities, and shift the SRAS curve rightward. D) do not affect the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities and therefore the SRAS does not shift rightward or leftward. E) increase the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities and shift the SRAS curve rightward.
According to liquidity preference theory, the slope of the money demand curve is explained as follows:
a. Interest rates rise as the Fed reduces the quantity of money demanded. b. Interest rates fall as the Fed reduces the supply of money. c. People will want to hold less money as the cost of holding it falls. d. People will want to hold more money as the cost of holding it falls.