Define decreasing returns to scale, illustrating your definition with isoquants. What are some reasons why firms might experience decreasing returns to scale?
What will be an ideal response?
Decreasing returns to scale occur when a proportional change in a firm's inputs produces a less than proportional change in output. This is illustrated in Figure 7.9:
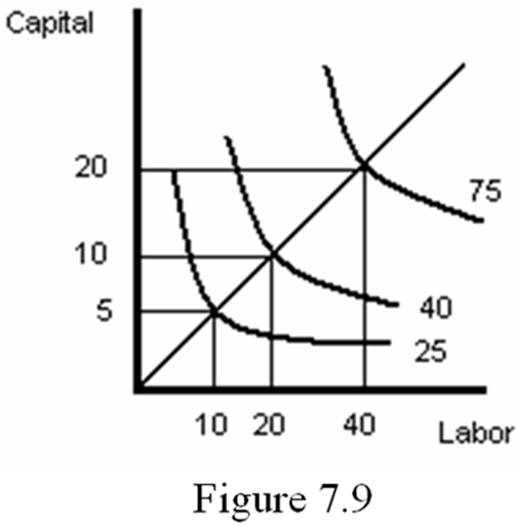
The firm is initially employing 10 workers and 5 units of capital to produce 25 units of outputs. When both inputs are doubled to 20 workers and 10 units of capital, output increases to 40 units (less than twice the original level). Decreasing returns to scale can occur because there is a fixed input that the firm fails to take into consideration. Also, decreasing returns can result from the fact that it is difficult to manage a large firm effectively.
You might also like to view...
The European Union established a cap-and-trade system which was designed to
A) eliminate air pollution and greenhouse gases by the year 2020. B) reduce carbon dioxide emissions. C) remove all taxes from polluting industries. D) provide fast growing developing countries with the technology to reduce their carbon emissions.
Agricultural staples of the colonial South included:
a. rice. b. tobacco. c. indigo. d. All of the above.
What is marginal analysis?
Job search
a. and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health both create frictional unemployment. b. creates frictional unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health creates structural unemployment. c. creates structural unemployment, while firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health creates frictional unemployment. d. and firms paying wages above equilibrium to improve worker health both create structural unemployment.