Refer to the table. A total output of 3 units of capital goods and 4 units of consumer goods:
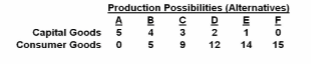
Answer the question on the basis of the data given in the following production possibilities
table:
A. is irrelevant because the economy is capable of producing a larger total output.
B. will result in the maximum rate of growth available to this economy.
C. would involve an inefficient use of the economy's scarce resources.
D. is unobtainable in this economy.
C. would involve an inefficient use of the economy's scarce resources.
You might also like to view...
The central difference between the structural stagnation hypothesis and the secular stagnation theory is that:
A. structural stagnation applied in the 1940s, and secular stagnation applies today. B. structural stagnation focuses on globalization, while secular stagnation focuses on declining investment. C. structural stagnation focuses on declining investment, while secular stagnation focuses on globalization. D. structural stagnation is a hypothesis, while secular stagnation is a theory.
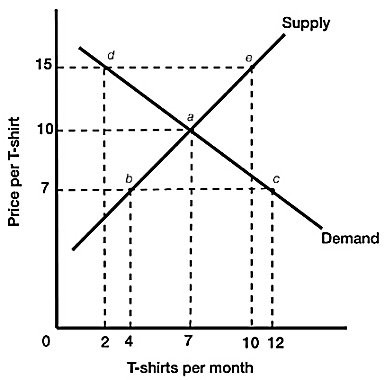
 Figure 3.3 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $7, we would expect that:
Figure 3.3 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $7, we would expect that:
A. demand will decrease until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. B. supply will increase until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. C. price will increase until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. D. there will be no change in the price since the market is in equilibrium.
Which one of the following is an example of discretionary fiscal policy used to correct a recessionary gap?
A. an increase in the money supply by the Federal Reserve B. a decrease in government expenditures approved by Congress C. a tax decrease passed into law by Congress D. an agreement among major banks to raise interest rates
If there is an expectation that the price of a good will decrease in the next month, this would immediately
A. cause a movement along the demand curve to a (lower price, higher quantity) point. B. move its demand curve to the right. C. move its demand curve to the left. D. cause a movement along the demand curve to a (higher price, lower quantity) point.