A rational consumer should not consume more of a good when
a. total utility is decreasing
b. marginal utility is diminishing
c. one unit has already been consumed
d. income is decreasing
e. the price increases
A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the following graph. Which of the following statements is true?
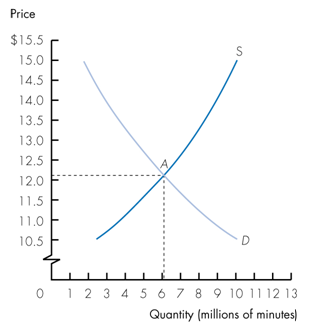
a. Equilibrium is shown at point A.
b. When the price is $13.50 a shortage exists.
c. When the price is $11.50 a surplus exists.
d. If the price is currently $11.00 then the price will fall over time.
If the social benefit is greater than the private benefit in a particular market, then the socially optimal equilibrium will be at a quantity:
A. greater than the private level. B. equal to the private level. C. less than the private level. D. greater than or less than the private level, depending on the size of the external costs.
If the cost efficiency of input A is 45 pounds per $1 of cost, and the cost efficiency of input B is 40 pounds per $1 of cost, then input A is more cost-efficient than input B.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
A real depreciation will initially cause a reduction in output when which of the following holds?
A) the Marshall-Lerner condition B) the J-Curve effect C) net exports are initially zero D) net exports are initially negative E) net exports are initially positive