Moral hazard:
A. is a normative judgement about the moral choices made by economic agents.
B. is about actions and occurs after the parties have voluntarily entered into an agreement.
C. is always present when adverse selection arises.
D. All of these statements are true.
B. is about actions and occurs after the parties have voluntarily entered into an agreement.
You might also like to view...
The MU/P equalization principle means consumers will spend their income (budget) so that the MU/P ratio of the goods consumed is
a. zero for each good b. higher for goods the consumer wants the most (highest marginal utility) c. maximized for the goods the consumer wants the most (highest marginal utility) d. higher than TU/P e. the same for each good
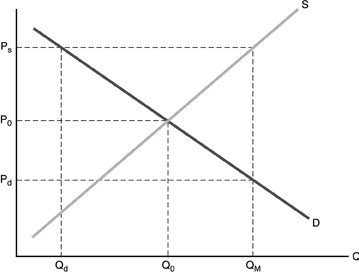 Refer to the above figure. Medicare subsidies have increased the price of medical services to Ps. The perceived price on the part of consumers is
Refer to the above figure. Medicare subsidies have increased the price of medical services to Ps. The perceived price on the part of consumers is
A. Ps. B. P0. C. Pd. D. undetermined without more information.
In the Stackelberg model, the leader has a first-mover advantage because it
A) has lower costs than the follower. B) commits to producing a larger quantity. C) reacts to the follower's decision. D) differentiates its output.
Refer to the above table. At a wage rate of $23 per worker, the firm will choose to employ:
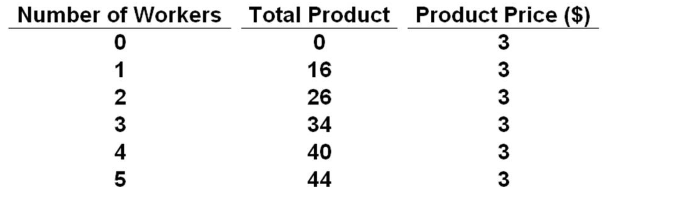
A. 2 workers
B. 3 workers
C. 4 workers
D. 5 workers