Simple Pendulum: A ball swinging at the end of a massless string, as shown in the figure, undergoes simple harmonic motion. At what point (or points) is the magnitude of the instantaneous acceleration of the ball the greatest?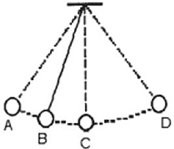
A. C
B. A and D
C. A and C
D. A and B
E. B
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Galaxies seem to be made mostly of dark matter. One type of evidence for this comes from observations of
A) the redshift in the light from the explosions of distant supernovas. B) the redshift in the light from the earliest galaxies in the universe. C) Both of the above. D) the speeds at which gas clouds orbit the centers of galaxies. E) distant quasars.
Which of the following best explains the hypothesized phenomenon of black hole evaporation?
A) Particles (or anti-particles) are occasionally ejected from within the event horizon, causing the black hole to lose mass. B) Virtual particles created near the black hole are constantly annihilating each other, causing a very high temperature even if the black hole has no accretion disk. This high temperature provides escape velocity for the virtual particles, causing the entire "cloud" of virtual particles to expand away into space. C) Particles (or anti-particles) are created by a quantum mechanical effect near, but outside, the event horizon of the black hole. The law of conservation of energy maintains that the black hole must lose energy to "pay" for the creation of this mass. D) Black hole evaporation is a virtual process, meaning that it has been theorized by astrophysicists, but doesn't really occur.
A 0.28-kg stone you throw rises 34.3 m in the air. The magnitude of the impulse the stone received from your hand while being thrown is
a. 0.27 N s. b. 2.7 N s. c. 7.3 N s. d. 9.6 N s. e. 34.3 N s.
Igneous rocks are formed by the
A) melting and transformation of minerals in Earth's interior. B) cooling and crystallization of molten magma. C) partial crystallization of granitic magma. D) cooling and crystallization of molten lava in Earth's interior.