What diffraction technique would you use to determine the atomic positions of hydrogen in uranium hydride?
(a) X-ray diffraction
(b) High-energy electron diffraction
(c) Low-energy electron diffraction
(d) Neutron diffraction
(d) Neutron diffraction
You might also like to view...
Addition by 1. Components: Three forces,  1,
1,  2, and
2, and  3, all act on an object, as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of the forces are: F1 = 80.0 N, F2 = 60.0 N, and F3 = 40.0 N. The resultant force acting on the object is given by
3, all act on an object, as shown in the figure. The magnitudes of the forces are: F1 = 80.0 N, F2 = 60.0 N, and F3 = 40.0 N. The resultant force acting on the object is given by 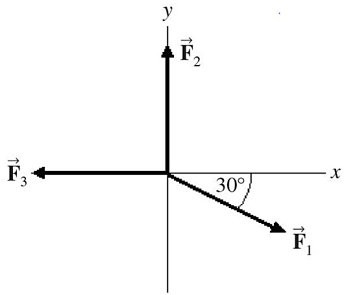
A. 180 N at an angle of 60.0° with respect to +x-axis. B. 60.0 N at an angle of 90.0° with respect to +x-axis. C. 20.0 N at an angle of 34.3° with respect to +x-axis. D. 35.5 N at an angle of 34.3° with respect to +x-axis. E. 40.0 N at an angle of 60.0° with respect to +x-axis.
Satellite Motion: Find the orbital speed of an ice cube in the rings of Saturn. The mass of Saturn is 5.68 × 1026 kg, and use an orbital radius of 1.00 × 105 km. (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2)
A. 19.5 km/s B. 27.5 km/s C. 13.8 km/s D. 9.40 km/s
Single-Slit Diffraction: A single thin slit forms a diffraction pattern when illuminated with monochromatic light. The fourth minimum of the pattern occurs at an angle of 32.0° away from the central maximum. At what angle does the fifth minimum occur?
A. 41.5° B. 41.0° C. 40.5° D. 42.0° E. 42.5°
Which one of the following statements is true?
A. Temperatures differing by 25? on the Fahrenheit scale must differ by 45? on the Celsius scale B. 40 K corresponds to ?40? C C. Temperatures which differ by 10? on the Celsius scale must differ by 18? on the Fahrenheit scale D. Water at 90? C is warmer than water at 202? F E. 0? F corresponds to ?32? C