Reabsorption involves what two methods of transport? Describe each. What determines which route a solute will take?
What will be an ideal response?
1. transepithelial transport: substances cross both apical and basolateral membranes of the tubule epithelial cell.
2. paracellular pathway: substances pass through the junction between two adjacent cells.
The permeability of the epithelial junction and the electrochemical gradient for the solute determines which route it will take.
You might also like to view...
Using the figure above, identify the labeled part.
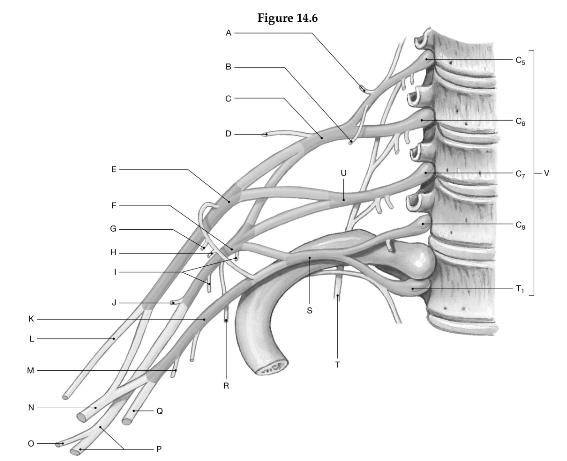
1. Label A: ______________________________
2. Label B: ______________________________
3. Label C: ______________________________
4. Label D: ______________________________
5. Label E: ______________________________
6. Label F: ______________________________
7. Label G: ______________________________
8. Label H: ______________________________
9. Label I: ______________________________
10. Label J: ______________________________
11. Label K: ______________________________
12. Label L: ______________________________
13. Label M: ______________________________
14. Label N: ______________________________
15. Label O: ______________________________
16. Label P: ______________________________
17. Label Q: ______________________________
18. Label R: ______________________________
19. Label S: ______________________________
20. Label T: ______________________________
21. Label U: ______________________________
22. Label V: ______________________________
Which of the following is NOT a systemic effect of IL-1 in response to infection or tissue injury?
A. Secretion of acute-phase proteins by the liver B. Stimulation of natural killer cells C. Induce fever D. Increased IL-2 receptor expression E. Stimulate inflammation
Smooth muscle tends to contract in response to being stretched.
a. True b. False
Myelinated axons in the CNS are known as:
A) dark matter. B) white matter. C) internodes. D) gray matter.