Opportunity cost is best defined as the value of
A. all of the other possible options that the decision maker could have chosen.
B. the alternative which the decision maker would choose if more resources were available.
C. what is gained from the alternative which is chosen.
D. resources that are given up to attain the alternative that is chosen.
E. the next best alternative that the decision forces one to give up.
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
Tracy and Amy are playing a game in which Tracy has the first move at X in the decision tree shown below. Once Tracy has chosen either the top or bottom branch at X, Amy, who can see what Tracy has chosen, must choose the top or bottom branch at Y or Z. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 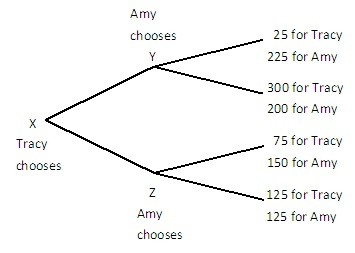 The equilibrium to the game results in ________ for Amy and Tracy relative to what they could get if they could solve their ________.
The equilibrium to the game results in ________ for Amy and Tracy relative to what they could get if they could solve their ________.
A. lower payoffs; credible threat B. lower payoffs; commitment problem C. higher payoffs; commitment problem D. lower payoffs; prisoner's dilemma
Networks are the result of product differentiation
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
With no change in fiscal policy, the budget
A. will run a surplus during a recession and a deficit during a boom. B. deficit will rise during a recession and fall during a boom. C. deficit will fall during a recession and rise during a boom. D. will remain unchanged by adverse economic conditions.
Aggregate demand decreases and real output falls but the price level remains the same. Which of the following factors most likely contributes to downward price inflexibility in the immediate short run?
A. The multiplier effect B. The wealth effect C. Fear of price wars D. Business taxes