Increased government spending is an example of:
A. expansionary fiscal policy.
B. contractionary fiscal policy.
C. expansionary monetary policy.
D. contractionary monetary policy.
A. expansionary fiscal policy.
You might also like to view...
As U.S. real GDP rises, wealthier households may decide to buy ________ foreign goods and assets, which would cause a(n) ________ of the U.S. dollar.
A. more; appreciation B. fewer; appreciation C. more; depreciation D. fewer; depreciation
The massive deficit in the U.S. current account primarily reflects the
A. excess of foreign investment in the U.S. over domestic private investment. B. excess of U.S. exports over U.S. imports. C. transfers of money home by U.S. citizens working in other countries. D. excess of U.S. imports over U.S. exports.
Refer to the graph shown. If the firm wishes to double output from 500 to 1,000: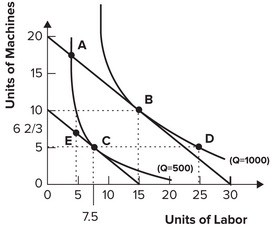
A. average total costs will rise. B. average total costs will remain the same. C. average total costs will fall. D. it is impossible to determine what will happen to average total costs.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 4.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.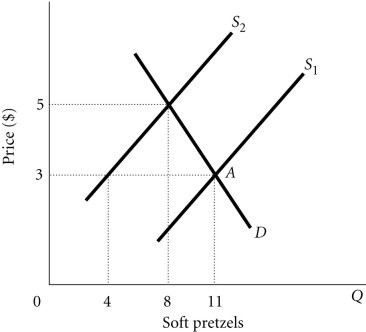 Figure 4.2Refer to Figure 4.2. The market is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of S2 and D, and supply shifts from S2 to S1. Which of the following statements is true?
Figure 4.2Refer to Figure 4.2. The market is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of S2 and D, and supply shifts from S2 to S1. Which of the following statements is true?
A. There is no need for price to serve as a rationing device in this case because the new equilibrium quantity is lower than the original equilibrium quantity. B. The market cannot move to a new equilibrium until there is also a change in supply. C. Price will still serve as a rationing device causing quantity demanded to rise from 8 to 11 soft pretzels. D. Price will still serve as a rationing device causing quantity supplied to fall from 8 to 4 soft pretzels.