Suppose you are offered a gamble in which you win $1,000 half the time but lose $1,000 half the time. If you are risk averter will you take the gamble?
What will be an ideal response?
Since you are as likely to win as to lose the $1,000, the average payoff on this gamble—its expected value— is:
0.5 ? $1,000 + 0.5 ? (-$1,000 ) = 0. If you are risk averse, you will not take the gamble because, for you, the possibility of losing $1000 outweighs the possibility that you will win, although both outcomes are equally likely.
You might also like to view...
If the U.S. government decreased its holdings of Mexican pesos, definitely
A) the capital and financial account would increase. B) the capital and financial account would decrease. C) there would be an increase in U.S. official reserves. D) there would be a decrease in U.S. official reserves.
Kiana’s country begins offering free college education to its citizens. This will most likely impact its production possibilities curve by ______.
a. causing it to spike b. shifting it outward c. shifting it inward d. causing it to trend downward
The way the government keeps price floors in effect is by _____.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Using Figure 1.6, we know the production of 90 units of soda and 1 unit of pizza is 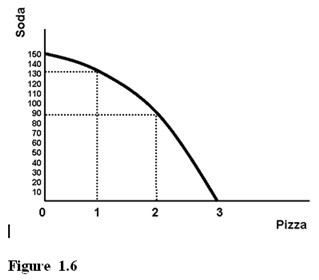
A. impossible because we have the resources but do not have the technology. B. possible, but there would be unemployed resources. C. possible, but only if all resources were fully employed. D. impossible because we have the technology but do not have the resources.