What is the Stolper-Samuelson theorem? What are the underlying conditions and assumptions for the theorem
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: The Stopler-Samuelson theorem concludes that opening trade splits a country into specific gainers and losers in the long run. Any event that changes relative product prices in a country raises the real return to the factor used intensively in the rising-price industry and lowers the real return to the factor used intensively in the falling-price industry. Four important conditions and assumptions are needed for the Stolper-Samuelson theorem: (1) the country produces positive amounts of two goods with two factors of production used in producing each good. One good is relatively land-intensive; the other is relatively labor-intensive. (2) Factors are mobile between sectors and fully employed overall in the economy. In addition, it is often assumed that total factor supplies (factor endowment sizes) are fixed. (3) Competition prevails in all markets. (4) Production technology involves constant returns to scale (e.g., if all factors used in producing a product double, then output of the product doubles).
You might also like to view...
A price-discriminating monopoly
A) sells a larger quantity than it would if it were a single-price monopoly. B) is illegal. C) cannot offer discounts. D) cannot control the price of its product. E) makes a smaller economic profit than it would if it were a single-price monopoly.
Under NAFTA, labor disputes and issues will be dealt with by the:
a. U.S. Department of Labor. b. North American Agreement on Labor Cooperation. c. National Labor Relations Board. d. U.S. Department of Justice.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 7.8 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 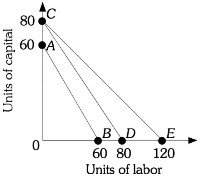 Figure 7.8Refer to Figure 7.8. The firm is currently along isocost CE. If the price of labor is $60, then the price of labor is
Figure 7.8Refer to Figure 7.8. The firm is currently along isocost CE. If the price of labor is $60, then the price of labor is
A. $40. B. $60. C. $80. D. $90.
A decrease in the quantity of money supplied at a given price level causes
A) no change in aggregate demand. B) a decrease in aggregate demand. C) an increase in aggregate demand. D) an increase in aggregate supply.