The difference between economies of scale and diseconomies of scale is that economies of scale ______, whereas diseconomies of scale ______.
a. are cost advantages experienced by large companies; are the benefits of remaining a small business
b. give the company an advantage over smaller competitors; are problems that come with growth
c. are advantages that affect a firm’s production in the short run; are experienced over the long run
d. are profits realized when the market price of outputs rises; are losses suffered when prices decline
b. give the company an advantage over smaller competitors; are problems that come with growth
You might also like to view...
As one moves downward on an indifference curve, the:
a. total utility from the consumption of a good decreases. b. total utility from the consumption of a good increases. c. the total satisfaction from consumption remains the same. d. the marginal utility from the consumption of a good increases. e. the total satisfaction from consumption decreases.
If firms offer an efficiency wage:
a. the quantity of labor supplied will exceed the quantity of labor demanded.
b. the quantity of labor demanded will exceed the quantity of labor supplied.
c. the quantity of labor supplied will equal the quantity of labor demanded.
d. absenteeism is expected to increase.
Refer to the figure below. In this game, the dominated strategy for Player A: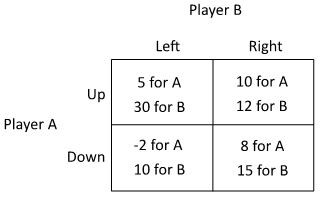
A. will depend on Player B's move. B. is to play down. C. is to play up. D. is to cooperate with Player B.
Suppose there are two small island countries: Avarice, which is populated by people who are completely self-interested, and Altruism, which is populated by people who have adopted social norms of generosity and cooperation. If two residents of Avarice play a prisoner's dilemma game, they are likely to:
A. reach the Nash equilibrium less often than would residents of Altruism. B. play their dominated strategies more often than would residents of Altruism. C. reach the Nash equilibrium more often than would residents of Altruism. D. never reach the Nash equilibrium.