Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 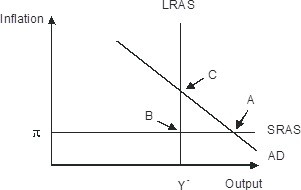
A. Rising; B; C
B. Falling; A; C
C. Falling; A; B
D. Rising; A; C
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 4-4. What is the value of the deadweight loss at a price of $18?
A) $100 B) $180 C) $660 D) $1,040
Refer to Table 19-5. The value of each automobile in gross domestic product equals
A) $7,000. B) $15,000. C) $18,000. D) $25,000.
Certain kinds of tropical fruits are impossible to grow outdoors in the United States. Suppose, however, that in order to create jobs in Wyoming, the U.S. government offered extensive subsidies to firms to produce bananas
With the subsidies, firms could build greenhouses and offer the fruit at world prices. A) The United States now has a comparative advantage in bananas. B) The United States has a comparative advantage, but is not competitive. C) The United States is competitive, but does not have a comparative advantage. D) The United States has a comparative advantage and is competitive. E) None of the above.
Assume that the central bank sells government securities in the open market. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and GDP Price Index in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic system returns to complete equilibrium
a. The real risk-free interest rate rises and GDP Price Index rises. b. The real risk-free interest rate falls and GDP Price Index falls. c. The real risk-free interest rate rises and GDP Price Index falls. d. The real risk-free interest rate and GDP Price Index remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.