At the point where actual inflation is equal to expected inflation,
A) the short-run Phillips curve intersects the long-run Phillips curve.
B) the short-run Phillips curve is the same as the long-run Phillips curve.
C) the unemployment rate is zero.
D) there is no short-run Phillips curve, as this situation only occurs in the long run.
A
You might also like to view...
In the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model,
a. the factors that cause the demand curves in both models to slope downward are the same. b. the factors that cause the supply curves in both models to slope upward are the same. c. the upward-sloping aggregate demand curve intersects the downward-sloping aggregate supply curve to determine the economy's price level and GDP. d. the upward-sloping aggregate supply curve intersects the downward-sloping aggregate demand curve to determine the economy's price level and GDP. e. the price level never changes even with shifts in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
Firm A produces and sells in a market that is characterized by highly differentiated consumer goods. Firm B produces and sells industrial products. Firm C produces and sells an agricultural commodity. Which firm is likely to spend the greatest portion of its total revenue on advertising?
a. firm A b. firm B c. firm C d. There is no reason to believe that any one of the three firms would spend a greater portion of its total revenue on advertising than the other two firms.
Use the figure below to answer the following question.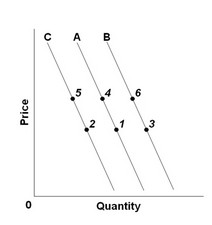 Refer to the three demand curves. A "decrease in quantity demanded" caused by a change in price would be illustrated by a change from
Refer to the three demand curves. A "decrease in quantity demanded" caused by a change in price would be illustrated by a change from
A. point 1 to point 6. B. point 2 to point 5. C. point 5 to point 1. D. point 6 to point 4.
A depreciation of the U.S. dollar
A. makes U.S. exports more expensive in terms of foreign currency and imports less expensive in terms of the dollar, increasing net exports. B. makes U.S. exports more expensive in terms of foreign currency and imports less expensive in terms of the dollar, decreasing net exports. C. makes U.S. exports less expensive in terms of foreign currency and imports more expensive in terms of the dollar, increasing net exports. D. makes U.S. exports less expensive in terms of foreign currency and imports more expensive in terms of the dollar, decreasing net exports.